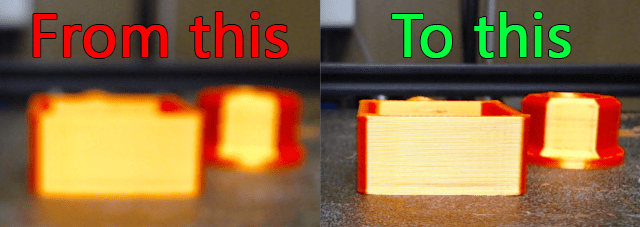
If you are like me you get annoyed with the constant focus tracking of your webcam in Klipper. This got me wondering if it was possible to turn off the autofocus, and after some research this is the method I came up with. I hope you find it as useful as I did. This worked perfectly for my C920, but it should work on other cameras as well. The method should probably also work on Octoprint, if that is what you are using.
1. First step is to install putty 51 if you are in windows and this will let you login to the raspberry pi via SSH. If you are on Mac you should use a similar program for that. (I'm no Mac user, so don't have any suggestions at the moment)
2. at the "Session" tab and "Host Name" field add fluiddpi.local, mainsail.local, whatevernameyouchose.local or your Raspberry Pi ip (You can find the ip in the administration panel of your router, which is usually the ip: 192.168.1.1, or something similar like 192.168.1.X), choose SSH, port 22, then click "Open".

3. Username is by default pi, and password raspberry (If you have changed these, input the values you've changed to)
You have to go to folder "mjpg-streamer", so you enter the command: cd mjpg-streamer/
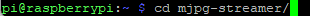
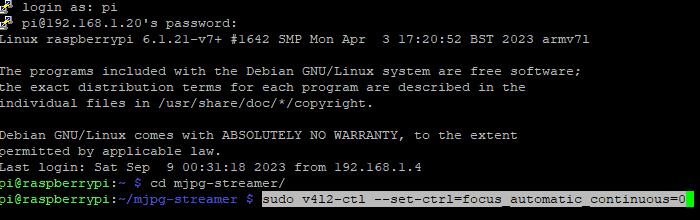
Now enter sudo v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl=focus_automatic_continuous=0 to disable auto focus
Open a window with your Klipper webcam, preferably with an object in the center of the bed and fine tune the manual focus..
so enter sudo v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl=focus_absolute=70 and change the number until the focus is ok.
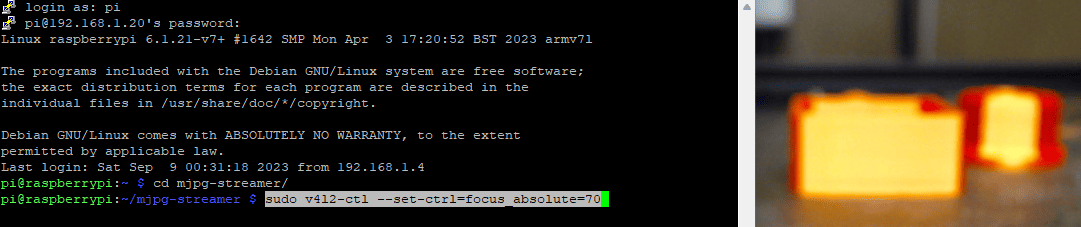
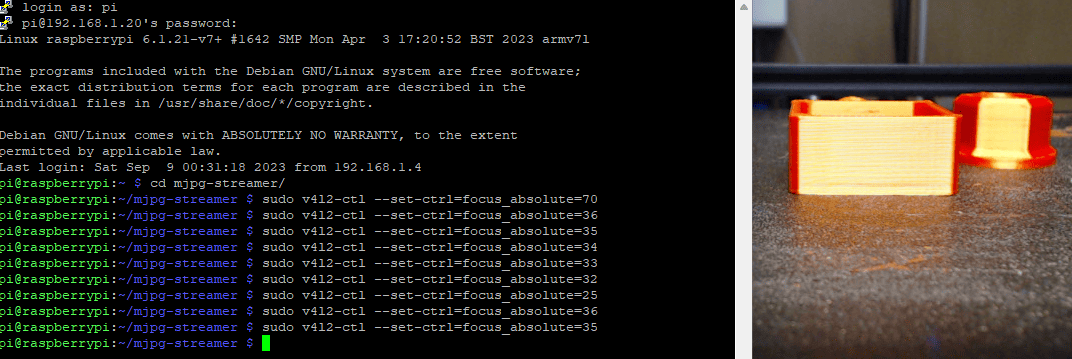
In this case, a number of 35, looks to be pretty good, so I'm running with that.
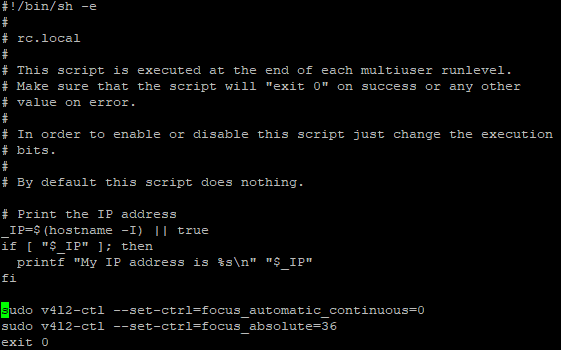
Now, you have your two commands that fine tune your camera. In order to run them every time you boot up your Raspberry Pi, you have to add them to the rc.local file:
a) enter sudo vi /etc/rc.local, then go to line last line "exit 0"
b) press shift+O and write your two commands (you can copy and paste with left click)..
if you mess up something press esc and :q! to quit
if you are fine press esc and :wq to save
It looks something like this:
Some additional info:
if you set focus_auto to 1 and let the webcam focus an object in the center you can take the "perfect" focus value..and then focus_auto to 0.
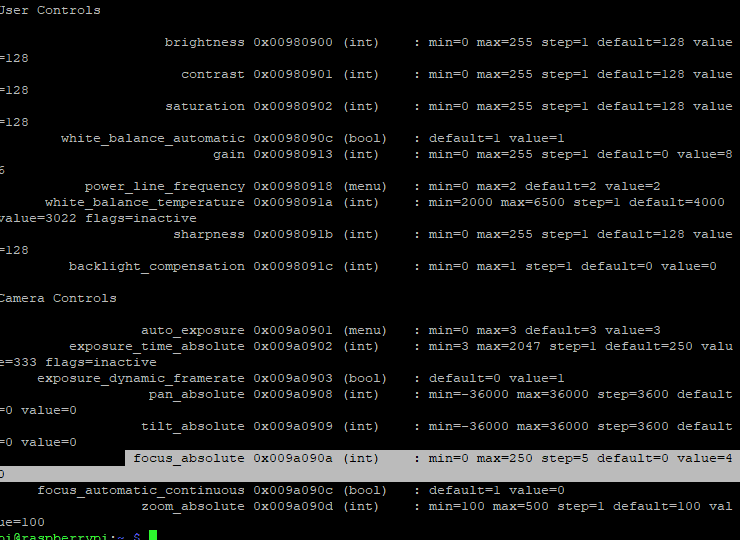
To find the value, You have to run the command sudo v4l2-ctl -l and you will see a list of settings for the webcam, in this case you should be looking for:
"focus_absolute (int) : min=0 max=250 step=5 default=8189 value=*"
The * in this case is your "perfect" value according to the camera. The reason I add this as additional info instead of including it in the main part, is that it didn't work too well for me. It gave me a value of 40 instead of the 35, I got to by looking at the webcam feed. This is probably because some other area of the printer, like my textured sheet kept the focus instead. This might be different for you though, so it's worth a try.
You can play with the other listed settings also..(like contrast with sudo v4l2-ctl --set-ctrl=contrast=200)
I hope you find this article useful. Have a great day everyone!

 Unlock with Patreon
Unlock with Patreon